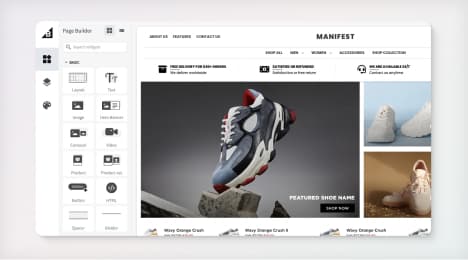
Watch Our Product Tour
See how BigCommerce helps you build and manage your online store with ease.
- Ecommerce Insights

6 Key Steps to Launch Your Online Store
Explore our Launch Foundations series to get your BigCommerce store up and running quickly.
BigCommerce helps growing businesses, enterprise brands, and everything in-between sell more online.
Start growing your ecommerce business even faster.
High-volume or established business? Request a demo