
Ecommerce insights on the go
Tune in to the Make it Big Podcast — our thought leadership audio series for retailers, entrepreneurs and ecommerce professionals. You'll get expert insights, strategies and tactics to help grow your business.

A Painless Guide to Ecommerce Accounting


A Painless Guide to Ecommerce Accounting
Get The Print Version
Tired of scrolling? Download a PDF version for easier offline reading and sharing with coworkers.
A link to download the PDF will arrive in your inbox shortly.
When you ask an ecommerce business owner, what’s the least favorite part of their job — most will say ‘accounting.’
(If you are that rare gem who loves accounting, virtual high-five to you!)
And yet 41% of small business owners handle their books without any help.
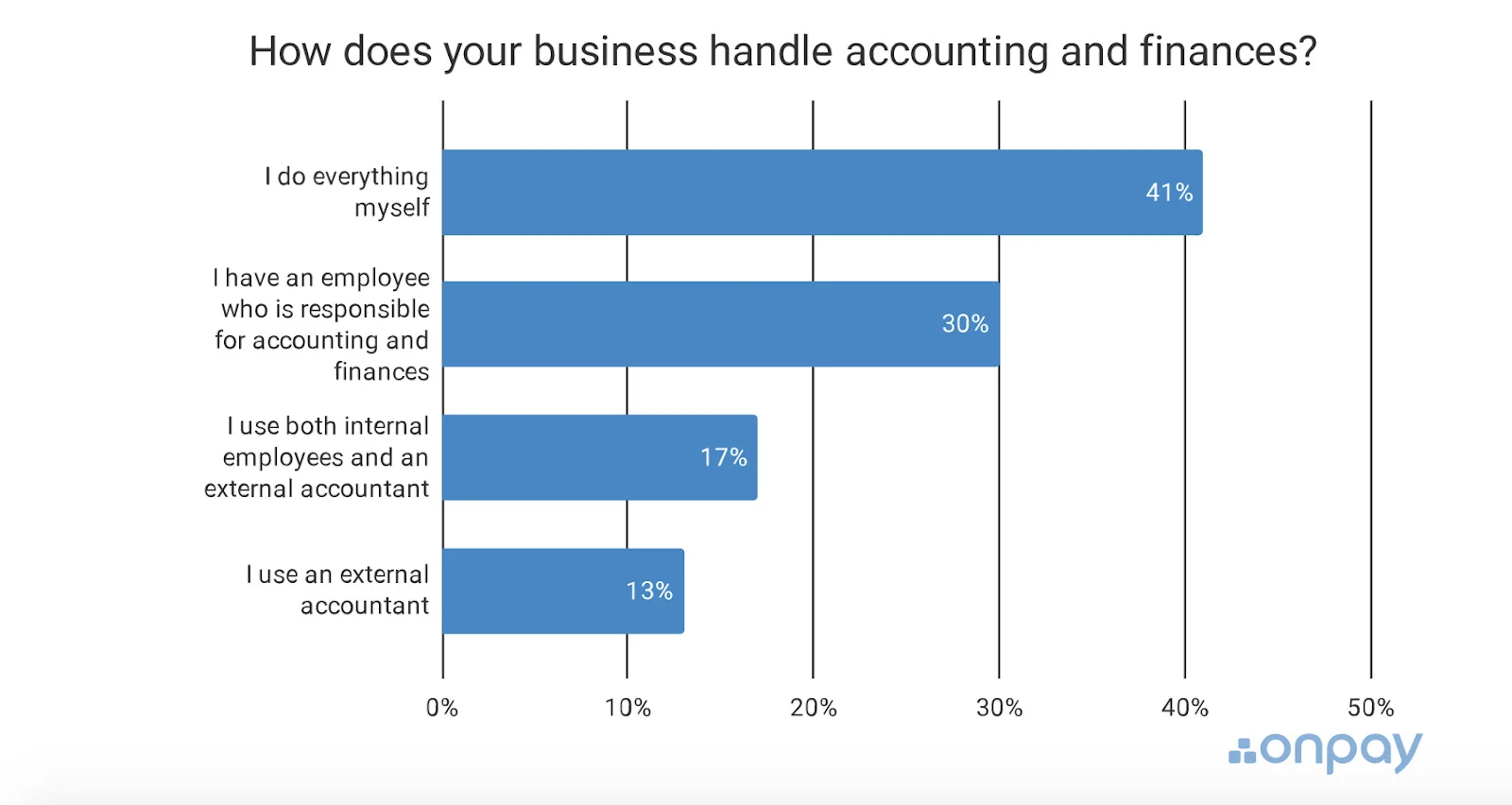
Source: OnPay
But here’s the deal: as your ecommerce business grows, your finances will get more complicated. Sales, returns, supplier payments, banking fees — all of the in-and-out money movements will need to be properly categorized, analyzed, and then reported to the tax authorities.
Without proper accounting systems in place, you can quickly get overwhelmed with all the financial data you are up against.
Also, compound this with the fact that:
19% of those who perceived themselves as having high financial literacy are financially literate.
We don’t mean to discourage you from doing your own accounting with that data.
But we really want to get your full attention. Because accounting is important. But learning to love it is hard. In this guide, we explain everything you need to know about ecommerce accounting without any dread.
Ecommerce Accounting vs Bookkeeping: What’s the Difference?
Let’s start with the basics and recap who is who in the accounting field.
Bookkeeping is the baseline accounting practice of maintaining a neat record of financial documents and transactions. The purpose of this practice is to describe and organize the state of your finances.
Key bookkeeping tasks include:
Transaction categorization.
Invoicing.
Account reconciliation.
Balance sheets preparation.
Payroll management.
Account payables and receivables management.
Accounting is a practice of analyzing all the financial records, produced by the bookkeeper, to create financial reports, models, and forecasts. So that you could understand the current level of your finances and plan for the future.
The main accounting tasks include:
Preparation of adjusted entries.
Financial information audits.
Tax planning and reporting.
Financial forecasting and risk analysis.
Preparation of financial statements, reports, and models.
The purpose of accounting is to equip you with financial knowledge to make smarter business decisions.
The 2 Types of Accounting for Your Ecommerce Business
Systemization is essential in accounting. To keep your ecommerce financials organized, you can use either of the two types of popular accounting systems.
1. Cash basis accounting.
When using the cash method of accounting, you add a new record whenever the cash lands in your bank account or leaves it as an expense. This way your books mirror all the transactional information, stored across your payment methods and bank accounts.
Here’s a quick example of cash basis accounting record:
Sales
Expense
Week 1
+$555 (T-shirt sales)
-$75 (shipping costs)
Week 2
+$200 (Hoodie sales)
-$65 (packaging fees)
Totals
$755
$140
Biweekly income: $615
Cash basis accounting is a ‘starter’ choice for most small ecommerce businesses. Because it’s a simple system to maintain — you just report on all money movements as they happen. Plus, you always know how much cash you have at your disposal right now.
Another boon of cash basis accounting is this: when reporting your business taxes at the end of the year, you won’t need to pay income taxes on the payments you haven’t received yet. So your tax bill can be smaller.
Cash basis accounting works for:
Small ecommerce sellers.
Maker businesses.
Products-on-demand stores.
However, this accounting method isn’t the best choice for larger ecommerce operations since it does not recognize future account receivables and accounts payables.
Due to that, avoid cash-based accounting if you:
Run an ecommerce business with high stock levels and multiple suppliers.
Plan to apply for financing or secure a loan for your business.
Want to bring auditors on-board and get audited financial statements.
2. Accrual method.
Accrual accounting, on the contrary, prompts you to record each sale or expense once it takes place, regardless of when the money reaches (or leaves) your bank account.
Let’s take a look at his sample record:
Date
Sales
Expenses
Week 1
$2,500 (online furniture sales)
$800 (subcontractor wage, due on Nov, 1st)
Week 2
$5,000 (in-store pick up, cash on delivery)
$100 (shipping costs)
Totals
$7,500
$900
Biweekly income: $6,600
The business made $2,500 in online sales. That money already landed in the bank account. But that bigger $5K check hasn’t cleared yet and is due to arrive on Week 3. Same with expenses — shipping costs were paid out immediately. But the contractor payment is due next month, meaning that $800 will be still sitting in the bank account till then.
Accrual accounting is often known as the traditional accounting method as it’s the system most financial institutions use. Think lenders, auditors, investors, tax planners, or anyone else interested in learning about the state of your company’s finances.
On the surface, accrual accounting seems more confusing than cash-basis accounting. You have to think about the money you haven’t earned yet (account receivables) and subtract costs you are yet to incur (account payables).
But once you get past that, this accounting system starts making more sense. Since it provides a more realistic representation of your business income every month. Plus it allows making more accurate financial projections as you take into account your present and future financial obligations.
The con of accrual accounting, however, is that this way of record-keeping shifts the focus from how much money you have to how much money you move. By counting in future payments/expenses, accrual accounting can make your operations look more profitable than they actually are. So you’ll need to keep closer tabs on your cash flow.
Should you switch to accrual accounting as an ecommerce entrepreneur?
The short answer is — yes. You’ll have to adopt this accounting system as your operations scale. Cash basis method for tax reporting is only permitted for companies with an average annual growth receipt of $5 million or less.
What You Need to Start Doing Accounting for Your Ecommerce Store
No matter which accounting system you go with first, you’ll need to have three things ready:
1. Business tax ID number.
If you operate as a corporation or a partnership, you’ll need to request an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. It’s a unique 9-digit identifier of your business to use in all your tax documents. You can apply for it online and receive it immediately by email. Sole traders can use their Social Security Number (SSN) for the same purpose.
2. Business bank account.
Keeping your business and personal finances separate is the first golden rule of accounting. Open a dedicated business bank account for your ecommerce store. Set up business versions of popular payment apps (e.g. PayPal). And make sure that you don’t spend any money from your business account on your personal needs (unless these qualify as deductible business expenses).
On the other hand, you can spend money from your personal account to cover your business expenses. You can then claim them back as ‘out of pocket’ expenses. Again, this should be reasonable business spending. Or you’ll risk regulatory questioning.
3. Accounting software.
Accounting apps and online services can save you heaps of time on sales recording, expense management, report generation, and other bookkeeping tasks. That’s why 50% of small businesses use them.
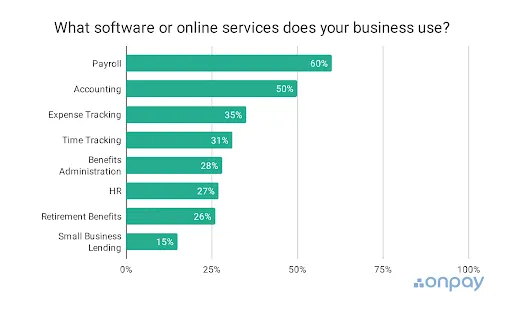
Source: OnPay
Popular accounting apps for small ecommerce stores are:
5 Important Ecommerce Accounting Tasks to Start With
With all the tools lined up, let’s take a look at the key accounting tasks you’ll need to do on a weekly/monthly basis:
Categorize all transactions.
Maintain a business budget.
Stay up-to-date with taxes.
Distinguish between returns and chargebacks.
Practice accurate recordkeeping.
Being diligent with each of them will help you understand your cash flow and prepare for the tax season.
Categorize All Your Transactions
Transaction categorization is the baseline practice of ecommerce bookkeeping. You should mark every transaction on your cash flow statement as either income or expense. Most accounting apps will auto-sort the transactions for you, so you should just review them and assign correct extra categories (e.g. salary, marketing, returns, etc).
Categorizing your transactions helps you estimate your:
Regular and one-off expenses
Monthly revenues
You can then use these figures to assess your online business income statement, plan for your taxes, and create a business budget.
Maintain Your Business Budget
A business budget is a tally of all your business spendings and other financial obligations, neatly summed up and stacked against your regular revenues. The total number tells you how much cash you need to break-even or make a profit.
The goal of a budget is to help you:
Monitor your cash flow patterns.
Stay atop of all recurring and unplanned expenses.
Know when to splurge and when to pedal back.
Set some income aside for the rainy day (and taxes).
Avoid or reduce business debt.
Stay focused on long-term financial goals.
Considering that 2020 was a tough year for small ecommerce businesses, budgeting can be a good practice to pick up and stick to. Here’s how:
1. Review your cash flow.
To budget effectively, you need to know when and where your money goes and how much comes in regularly.
Recording your spendings first since most of these will be recurring. Note how much you spend on:
Inventory purchases.
Supplier payments.
Employee salaries/subcontractors.
Packaging and handling.
Payment processing fees.
Business banking.
Software, apps, subscriptions.
Website hosting.
Advertising.
Taxes.
Refunds/returns.
Then factor in (un)planned one-off expenses. The total number you’ll get is your budget baseline — a sum you need to break even every month.
Since ecommerce sales volumes can zig and zag due to price fluctuations, changes in demand, seasonality, and other market conditions, your revenues can fluctuate. So you may end up having negative cash flow months — that is when you earned less than you’ve spent.
That’s another reason for having a budget and setting some extra income aside.
2. Create a weekly budget calculator.
To maintain positive cash flow, especially as at early growth stages, you need to be mindful of every cent you spend.
One way to do so is by setting up separate ‘pockets of cash’ for different weekly spending categories and updating them regularly. This way you’ll know exactly how much you’ve spent and can cut down on non-essential ones during the next week.
You can keep a similar spreadsheet where you list all your expenses and weekly revenue to estimate your cash flow dynamics:
Week 1
Week 2
Week 3
Inventory
$1,300
$300
$800
Payment processing
$55
$55
$55
Shipping
$25
$55
$95
Advertising
$500
$0
$200
Unplanned expenses
$150 (refunds)
$0
$500 (contractor)
Revenue (before tax)
$1,500
$1,800
$3,500
Cash Flow
– $530
+$1,390
+$1,850
Stay Up-to-Date with Taxes
Ecommerce business owners have two tax categories to mind — business income taxes and sales taxes.
Navigating sales taxes can be challenging since you need to factor in both:
State-level sales taxes (collected in 45 states and the District of Columbia).
Local sales taxes (collected in 38 states).
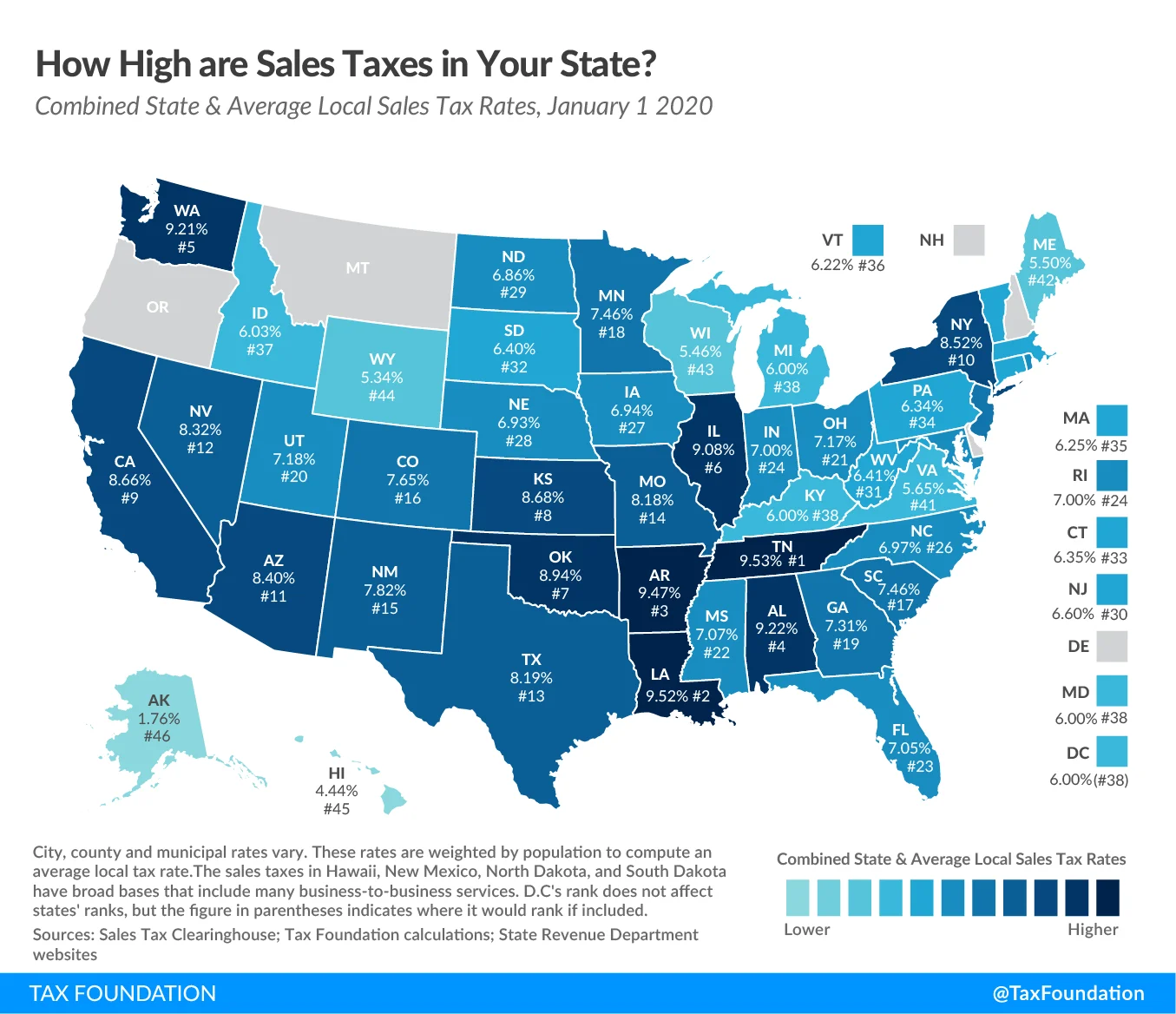
Source: Tax Foundation
1. Make sure your tax rates are correct for customers.
Depending on which ecommerce platform you are using for your store, you can either add all sales taxes manually to the checkout form or have these automatically calculated, based on the customers’ shipping address. The second option is less error-prone.
2. Pay estimated quarterly business taxes.
All ecommerce businesses who may owe more than $1,000 in taxes by the end of the year are expected to make quarterly estimated tax payments. The IRS calculates your dues based on the last return and expects payment according to the calendar.
3. File sales taxes.
You need to maintain clear records that you’ve collected sales tax for every customer invoice. All of these records will have to be filled with your local tax jurisdiction according to the due date. The filling frequency varies from state-to-state, but typically it’s by mid- or end of each month.
Distinguish Between Returns and Chargebacks
Customer returns and chargebacks are two different types of expenses that need separate recording.
1. Store return.
Ecommerce stores can have one or several return policies and this should reflect in your accounting:
Store credit: Record the original transaction as an expense and add it to the accounts payable list.
Full refund: Once the product arrives back to you, categorize the refund transaction under “Returns and Allowances” and subtract it directly for your revenue.
2. Store chargeback.
Chargebacks happen when a customer disputes a transaction with their bank by claiming that it was fraudulent. Sadly, such ‘friendly fraud’ accounts for 40%-to-80% of all fraud losses among e-tailers.
Categorize all the chargebacks as “Returns and Allowances.” Also, if the chargeback included an extra fee, mark it as a business expense.
Practice Accurate Recordkeeping for Your Ecommerce Store
Accounting is the art of maintaining financial records that tell a complete financial story of your business (for yourself and anyone else who asks).
Since you are self-reporting your financials and taxes to the authorities, you need to maintain proof of all your claims. That means you should store the following records for your ecommerce business accounting:
Receipts, bills, and invoices.
Canceled and bounced checks.
Previous tax returns.
W2 and 1099 forms.
Bank account, debit/credit card statements.
Account statements from online payment wallets.
Revenue records from your ecommerce platform such as BigCommerce.
All of these records should be kept for at least 3 years.
Seems like a lot? Well, it’s best to pay some extra for cloud storage, then face possible fines if you cannot back up your financial claims during an audit.
3 Quick Accounting Best Practices to Remember
Doing those five accounting tasks for your ecommerce store can be overwhelming, especially when you are just getting started.
Remember: you don’t need to go into financial guru mode and try to create fancy cash flow projections or use multi-step formulas to calculate your profitability index.
Keep your accounting simple and to the point:
1. Forecast for major expenses.
Keep a straight record of all regular account payables, along with a weekly budget Excel spreadsheet. This way you’ll always know your dues and can work around with the remaining income to accommodate a bigger expense — a new warehouse building, more advertising, or extra inventory.
2. Set money (and time) aside for taxes.
Tax season can be hectic if you come offhanded. One-third of small business owners spend over 80 hours (= two work weeks) per year on preparing their federal tax returns. Your commitment to maintaining neat records throughout the year will pay off massively.
As for the money, put aside 30%-40% of your business income towards end-of-year tax payments.
3. Supervise your inventory management.
The US retail sector faces $50 billion in losses per year due to the unmoving inventory. Don’t add up to those numbers as unnecessary inventory buildup impacts your liquidity and will reflect badly on all your assets and your bottom line.
The same goes for raw materials — don’t be tempted to over-buy unless you know that you can make use of all the stock. Storage costs will end up overeating any type of bulk discount you are getting.
To run lean operations, set a minimal and maximum volume of inventory that you can keep, based on your budgets and cash flow projections.
The Two Common Ecommerce Accounting Problems To Account For
To get even better in doing your accounts, don’t get lured into the following behaviors:
1. Waiting till the last minute to review financial statements.
Don’t postpone expense categorization till the end of the month, or worse — end of the reporting year. With thousands of records to sift through, you will miss something important. That can be something minor such as an unclaimed deduction. Or a major omission that may require corrections in your tax returns.
What to do instead: Block 2-3 hours each month when you sit down and review all the financial documents, organize them by category, and then do a bank account reconciliation.
2. Missing errors (due to the lack of time).
When you do your books in a hurry, mistakes will creep in. Having errors in your bookkeeping records can eschew your financial projections and result in financial losses. If those are left unattended, they can pass onto your tax fillings. Then you’ll need to file an amended tax return. Which again, isn’t the most fun thing to do.
What to do instead: Automate your accounting to prevent manual mistakes and inconsistencies. Once you have a budget, hire a chief financial officer (CFO), CPA (certified public accountant), or an in-house ecommerce accountant to help you with tax reporting.
Wrapping Up
You don’t have to be a certified accountant to stay atop of your ecommerce finances.
With the right accounting system in place, a supporting accounting app, and proper diligence you can get a good hang of your accounting, and learn to love the practice of analyzing your financials. Especially, when those insights translate to higher income!

Tomas Laurinavicius is a co-founder of Content Writing Jobs, lifestyle blogger, content marketing consultant, and BigCommerce researcher from Lithuania. He writes about lifestyle design, productivity, and entrepreneurship on his blog and lifestyle design newsletter.


